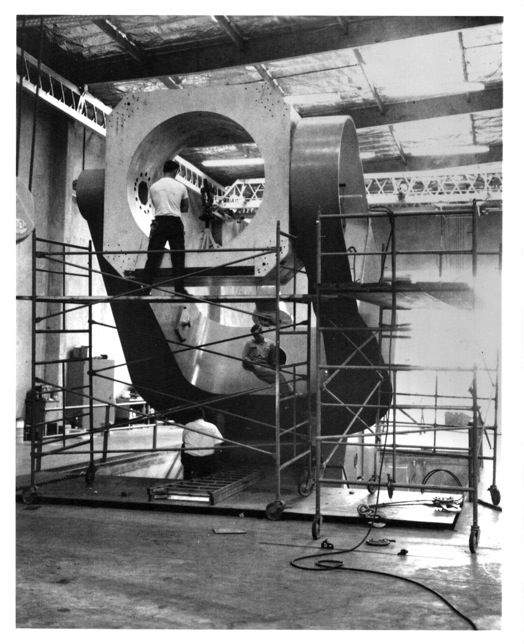
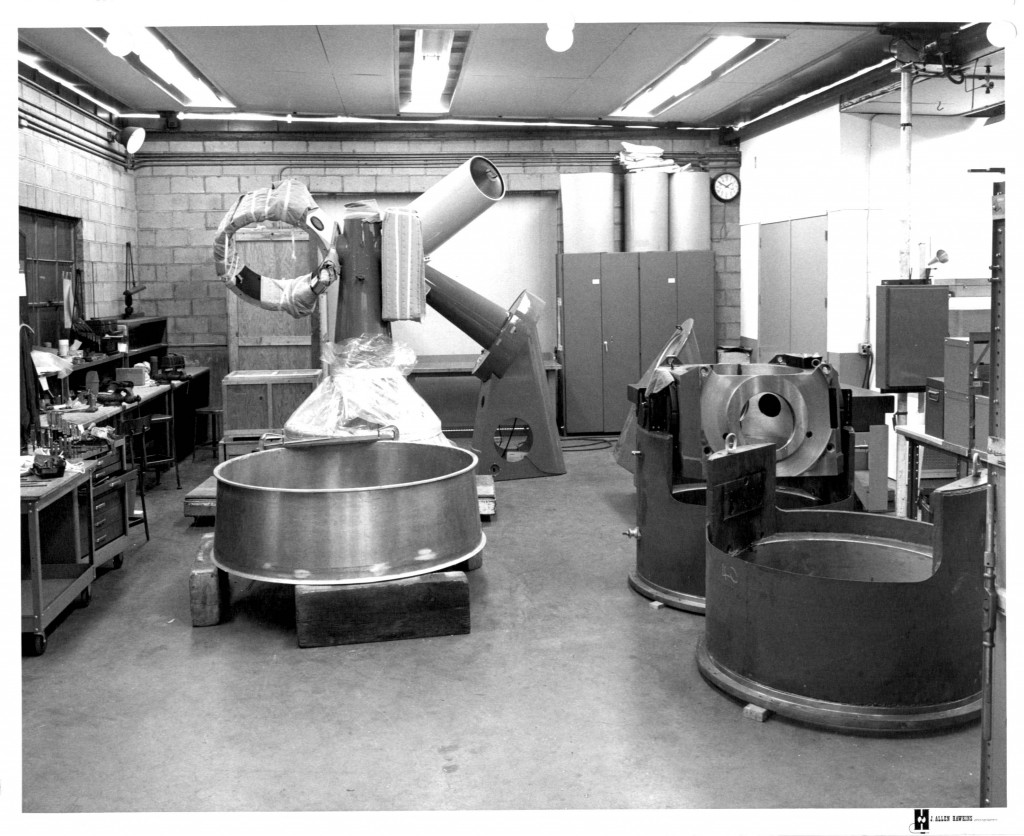
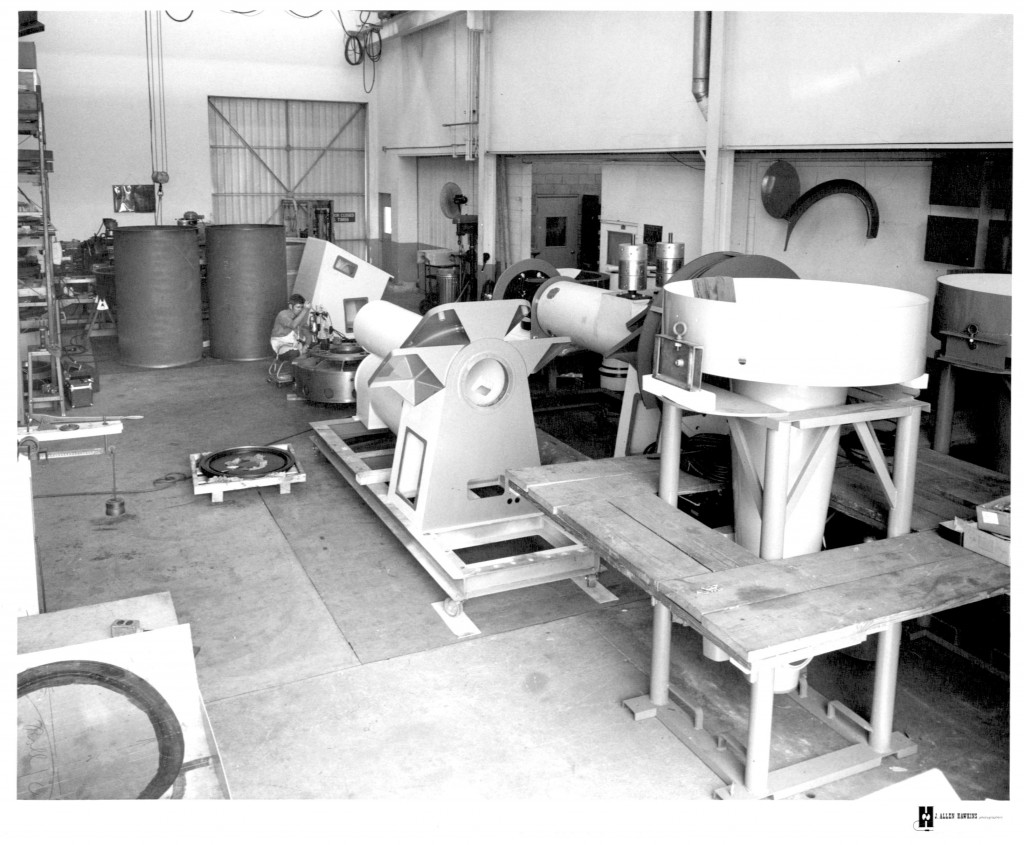
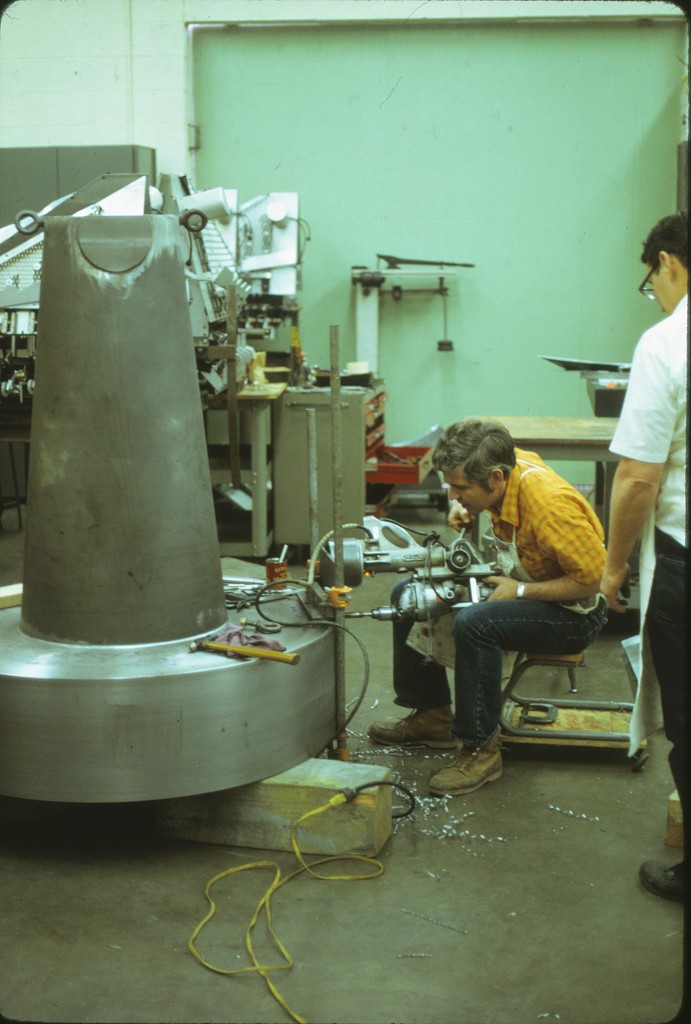
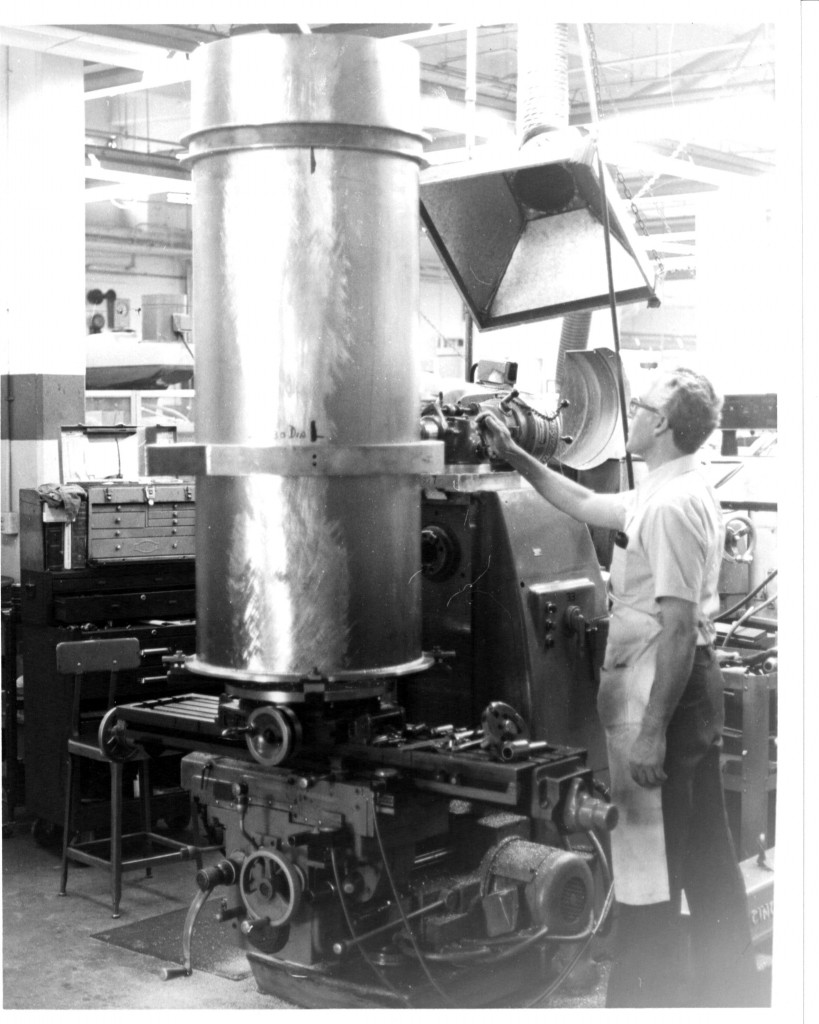
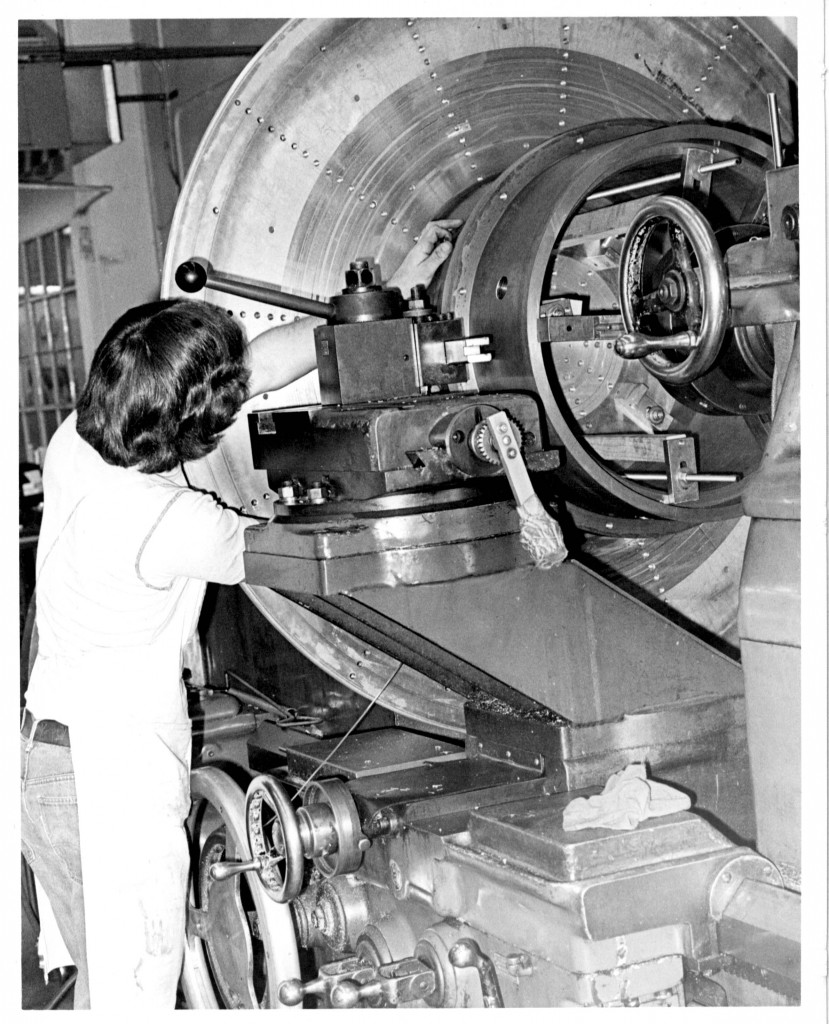
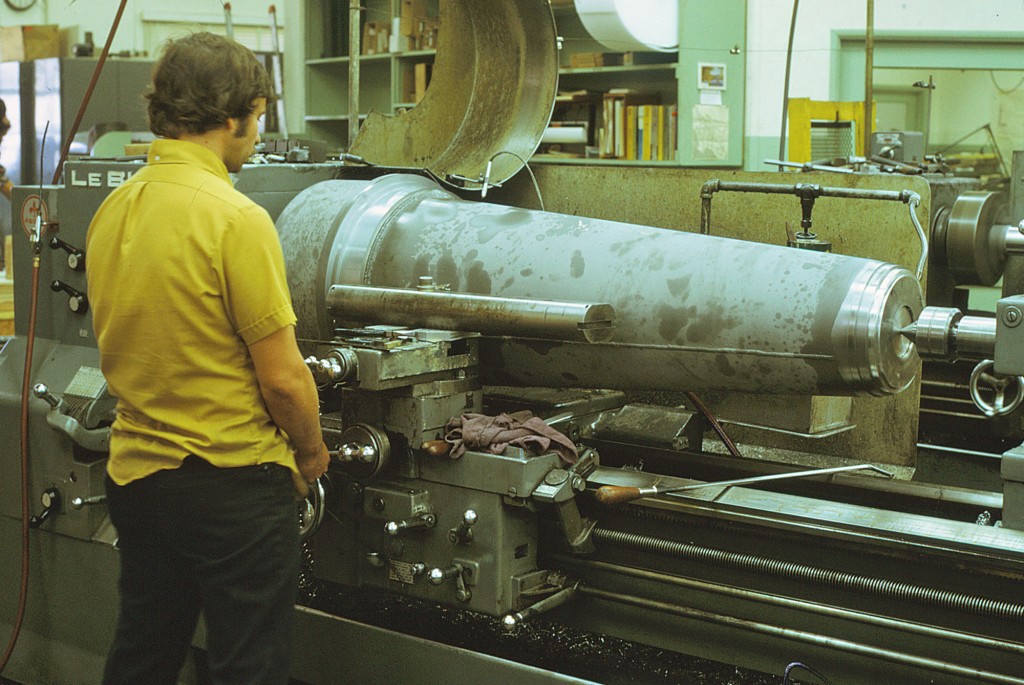
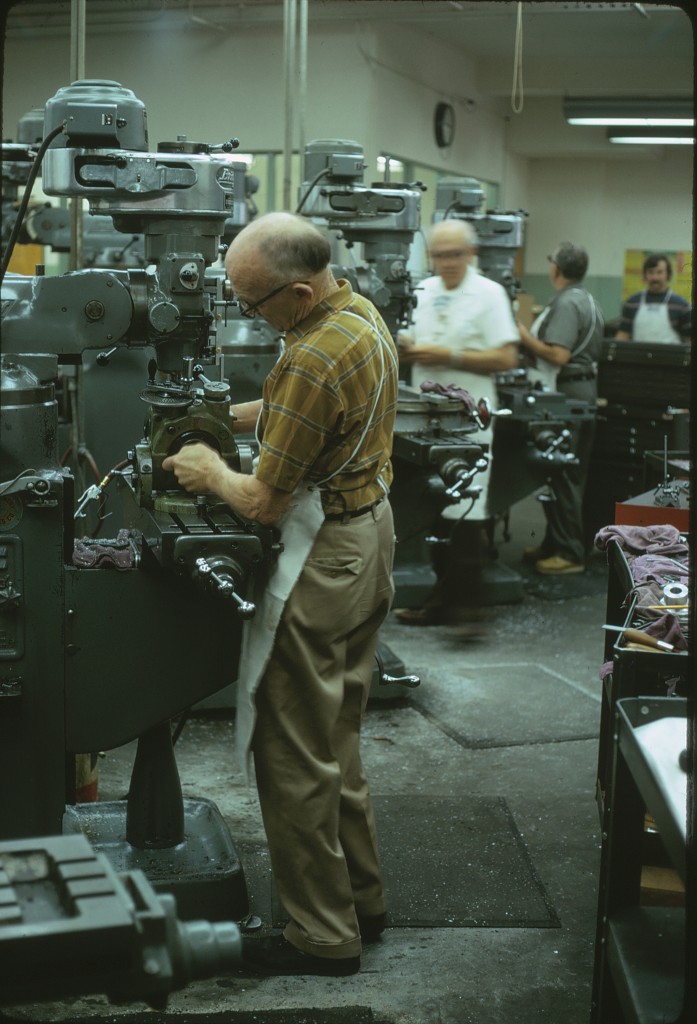
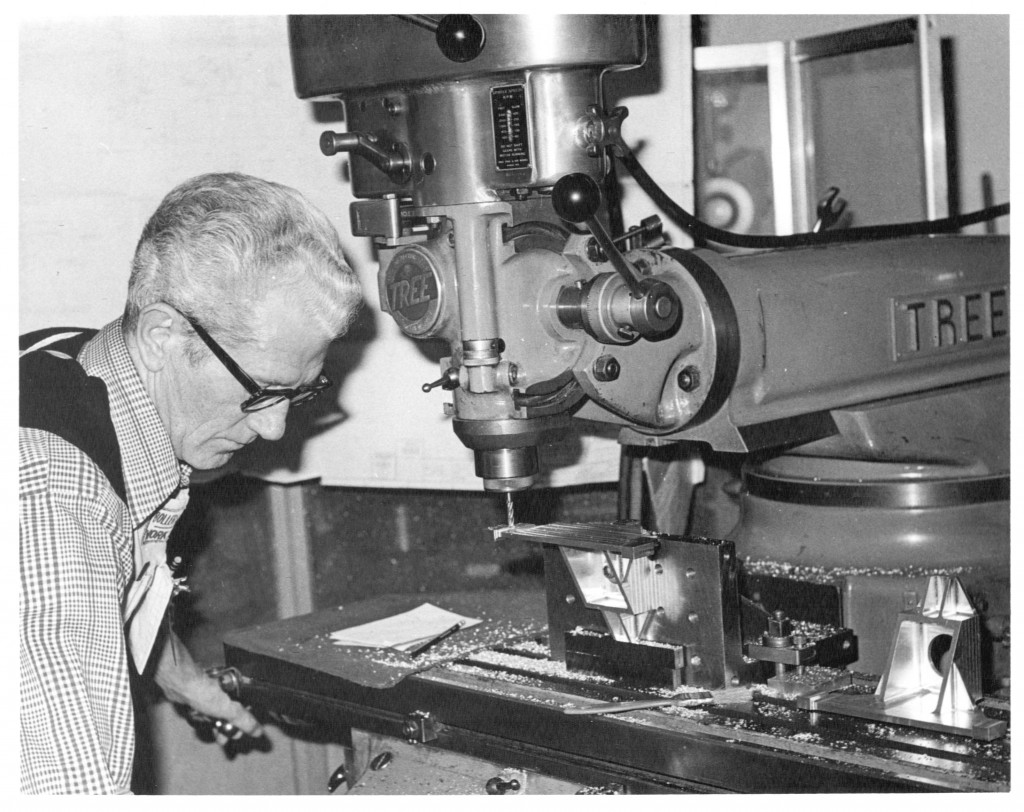
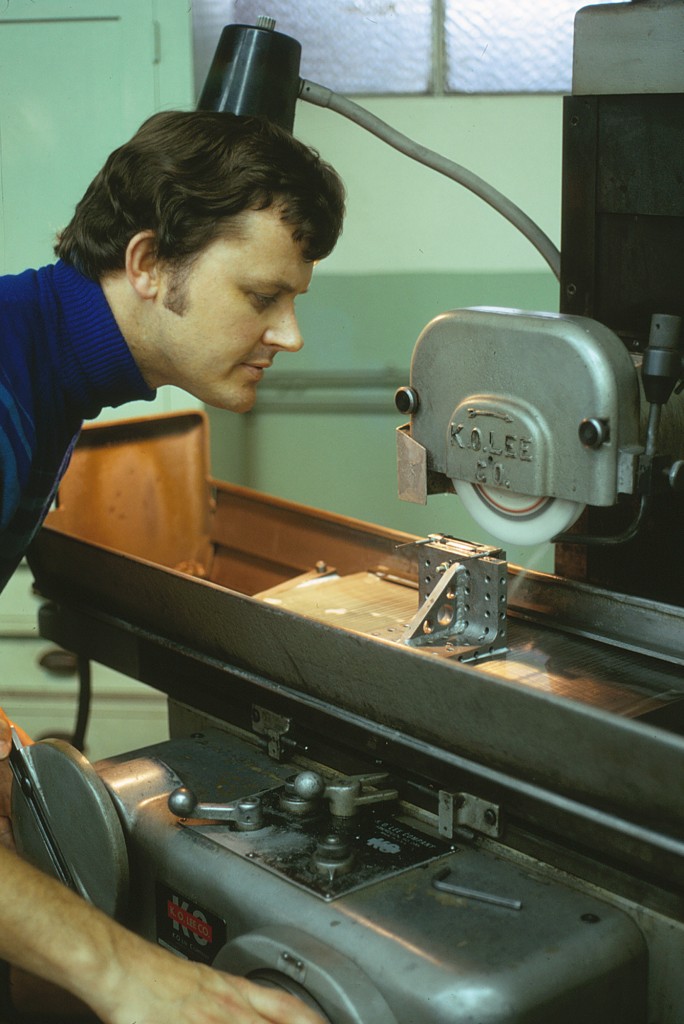
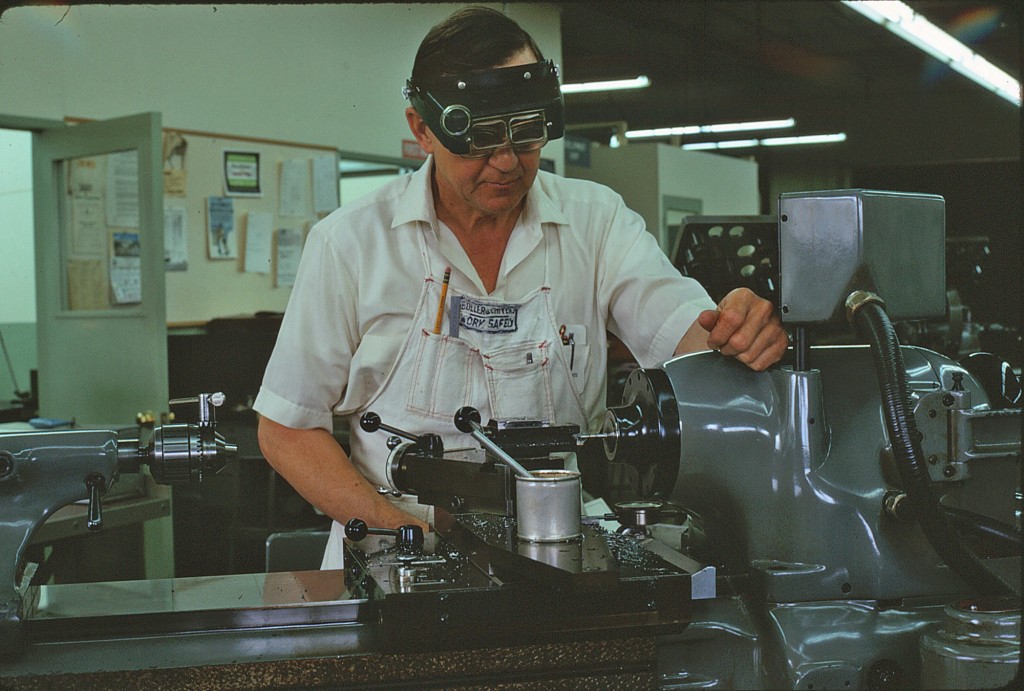
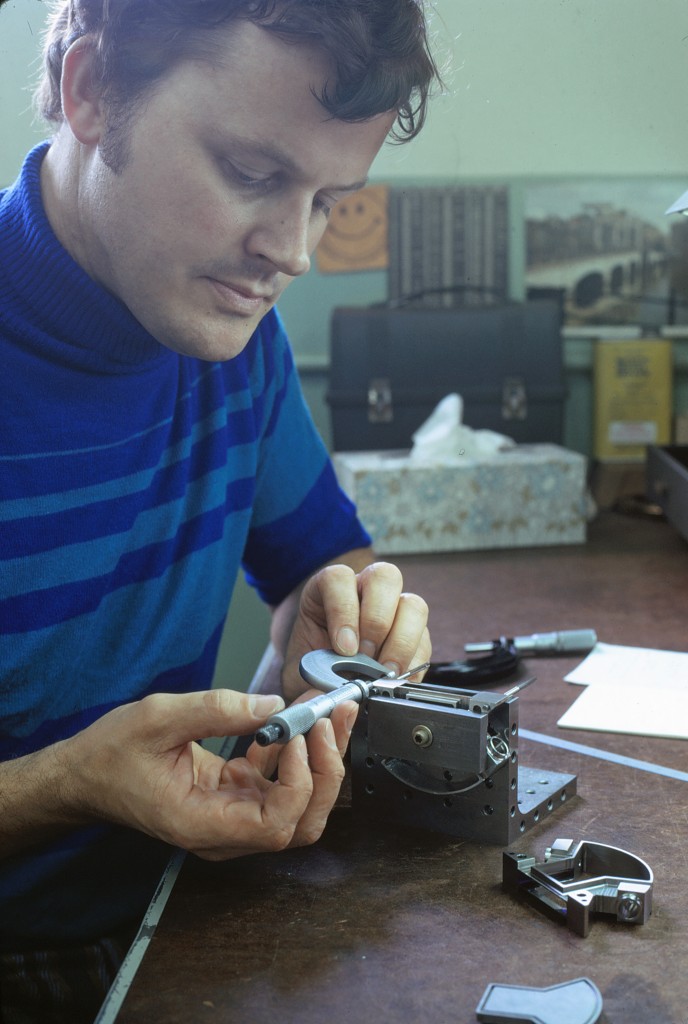
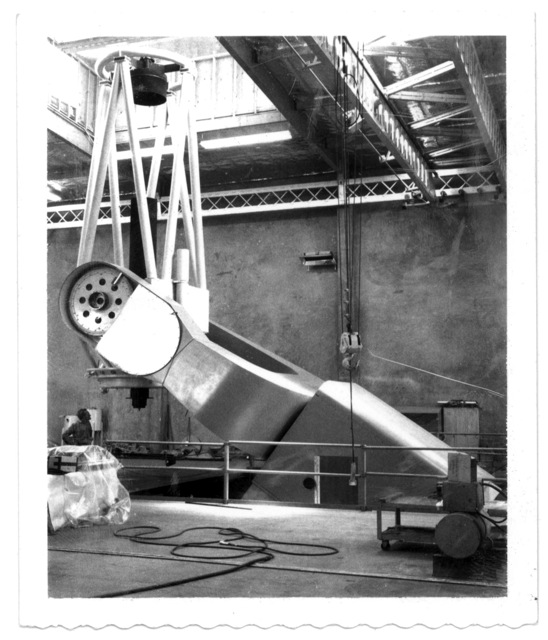
Declination Axle alignment at L & F Industries’ new assembly building
Declination Axle alignment at L & F Industries’ new assembly building
The 61-inch (1.55 meter) for the U. S. Naval Observatory at Flagstaff, Arizona was the first large aperture complete telescope designed, manufactured and installed by Boller & Chivens as a joint venture with L&F Industries.
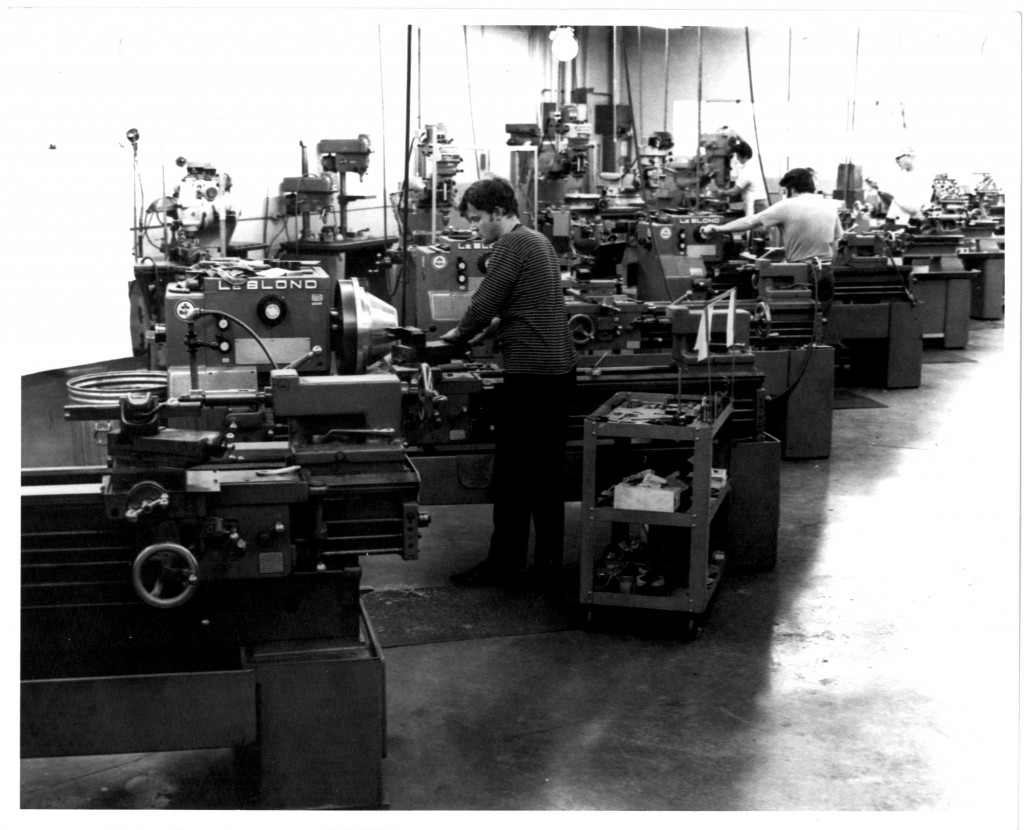
After that time, all telescopes with apertures up to 52-inch (91.32 meters) were assembled in a new Boller & Chivens assembly building at the South Pasadena plant.
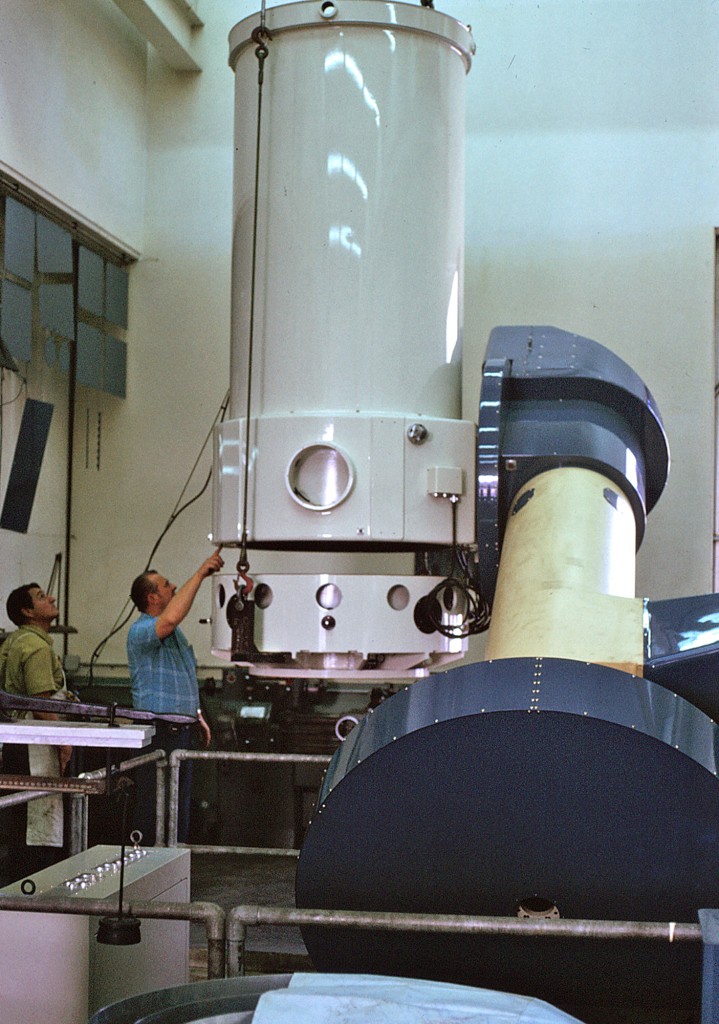
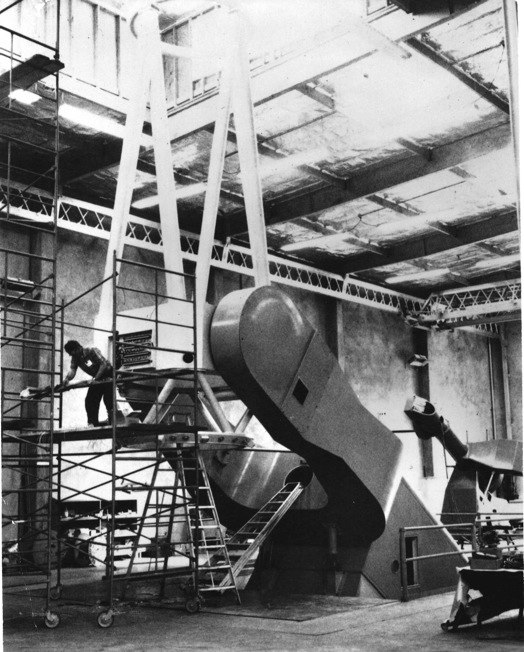
 Installation of upper tube with its Serrurier trusses and secondary mirror support ring
Installation of upper tube with its Serrurier trusses and secondary mirror support ring
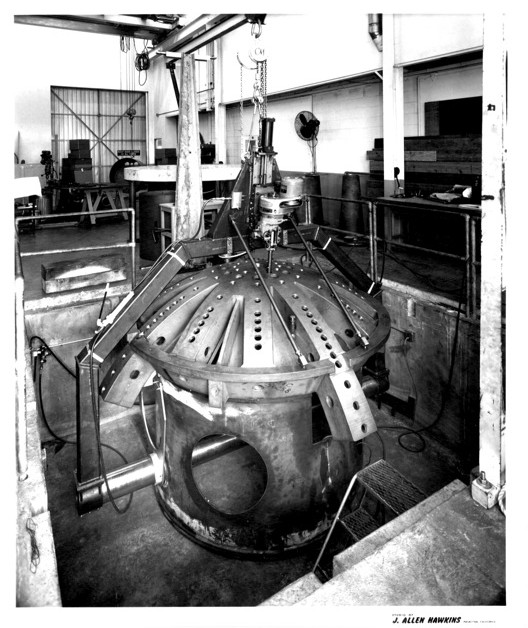
 Final assembly showing lower tube Serrurier trusses and wiring of the telescope
Final assembly showing lower tube Serrurier trusses and wiring of the telescope
In the background, the 40-Inch telescope for Siding Spring, Australia
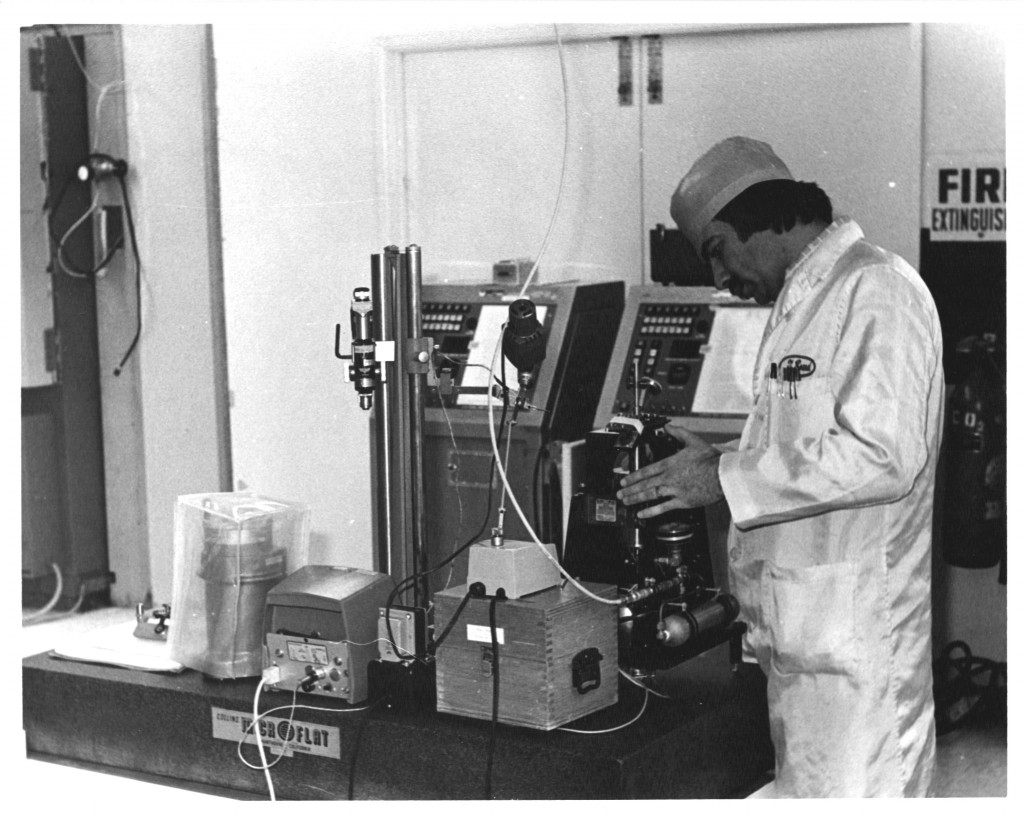
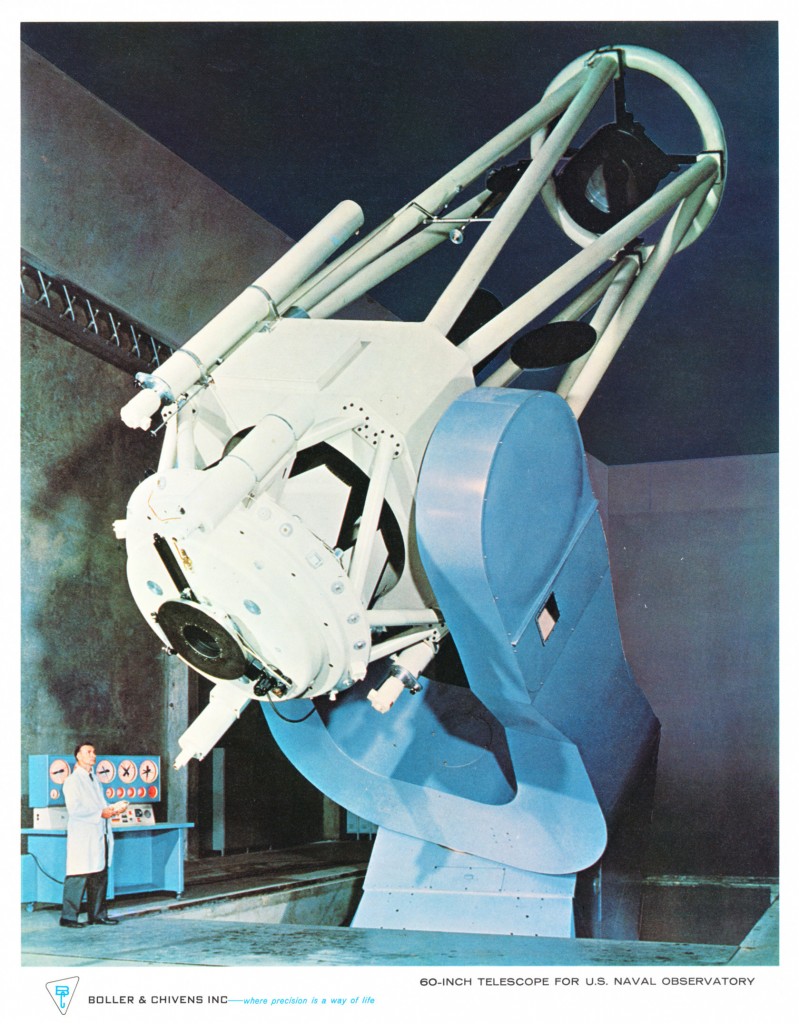 Harry Boller at the console showing the operation of the 61 Inch telescope using the remote control paddle.
Harry Boller at the console showing the operation of the 61 Inch telescope using the remote control paddle.

The 100″ Carnegie Institution of Washington will be located at Las Campanas Observatory, Chile
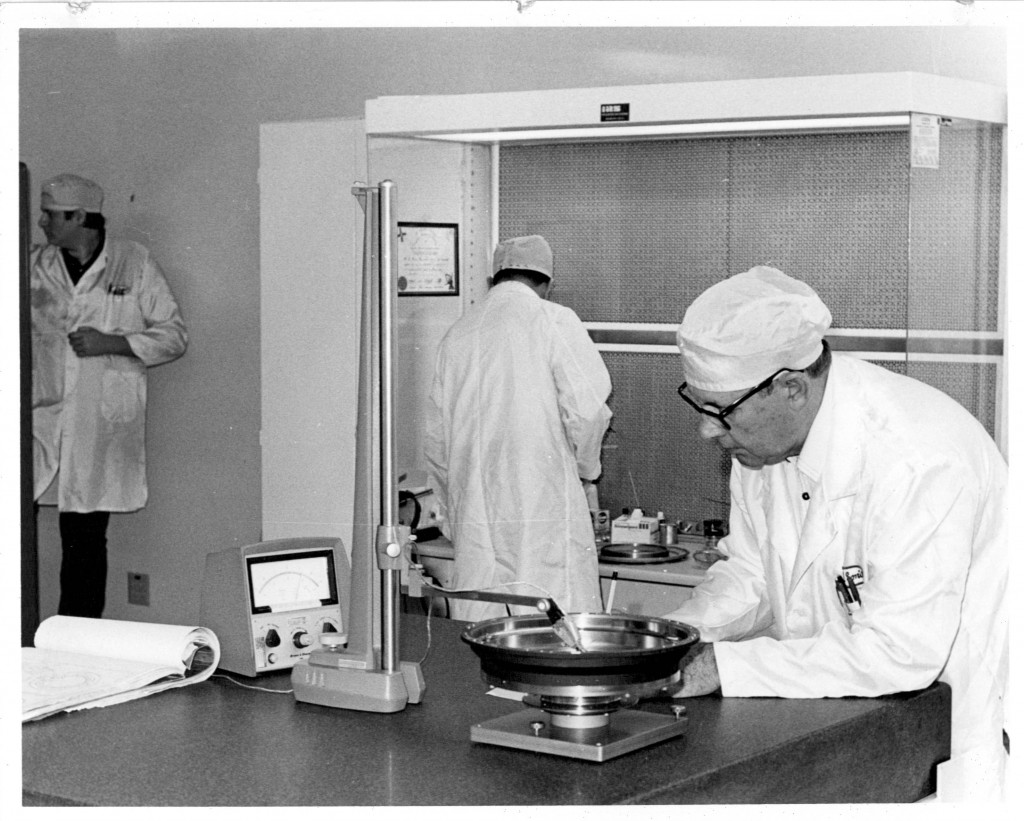
The telescope is being assembled by Boller and Chivens personnel in a telescope assembly pit at the L and F Industries assembly building.
In the foreground is Larry Steimle standing by the 100″ main double mirror secondary support system.
The main support ring ties the top Serrurier trusses together on the telescope tube assembly.
Mounted inside between two bearings on the centerline of the main support ring, is an inner support ring that can rotate 180 degrees.
Plunger type pins on opposing sides assures that the inner ring when rotated will stop exactly at 180 degrees.
The inner ring has an assembly containing two separate opposing secondary mirrors. This allows setting up two different observing f/stop observing ratios. Either one of the two different secondary mirrors can quickly be optically positioned for different observing conditions.
 Declination Axle alignment at L & F Industries’ new assembly building
Declination Axle alignment at L & F Industries’ new assembly building Installation of upper tube with its Serrurier trusses and secondary mirror support ring
Installation of upper tube with its Serrurier trusses and secondary mirror support ring Final assembly showing lower tube Serrurier trusses and wiring of the telescope
Final assembly showing lower tube Serrurier trusses and wiring of the telescope Harry Boller at the console showing the operation of the 61 Inch telescope using the remote control paddle.
Harry Boller at the console showing the operation of the 61 Inch telescope using the remote control paddle.